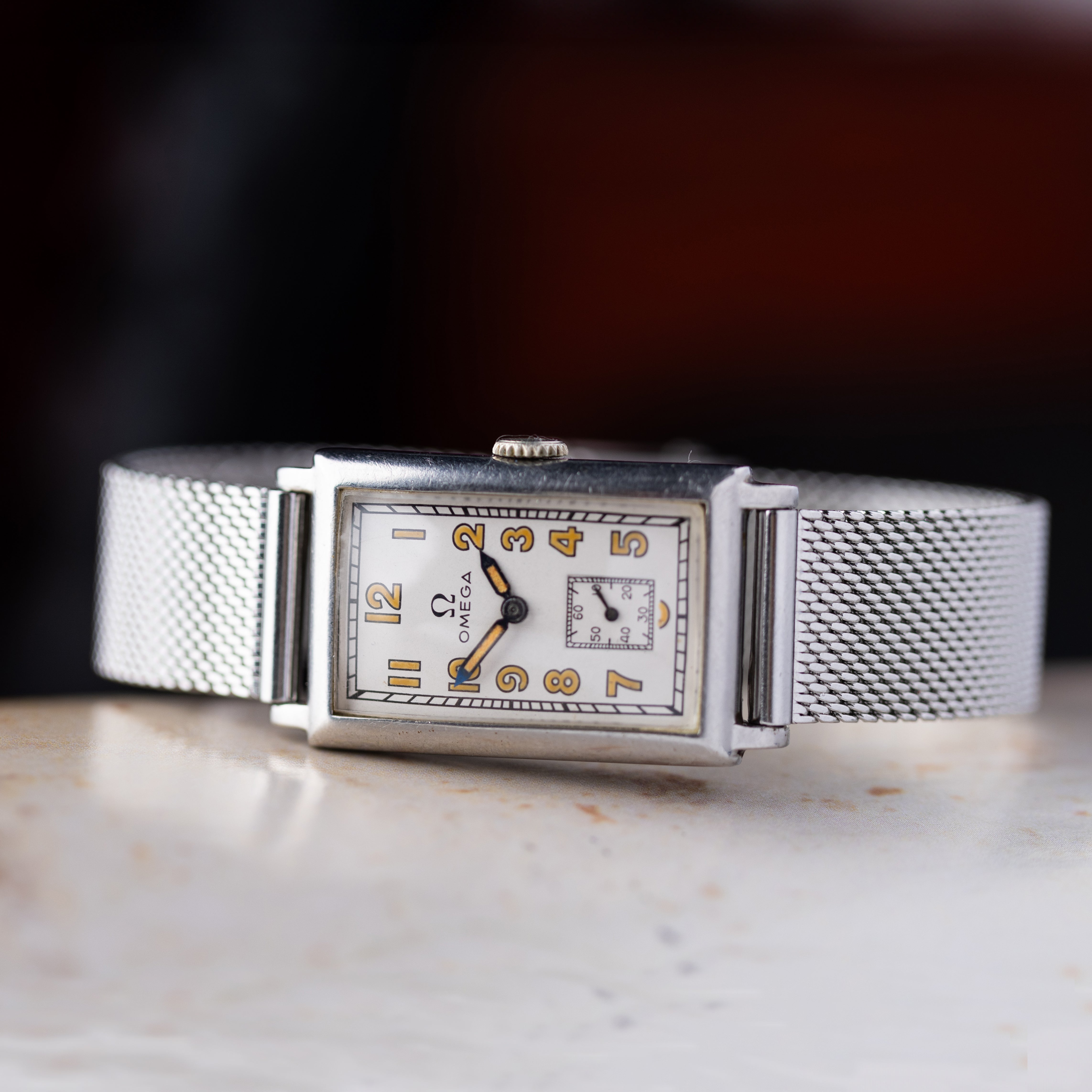
Radium dial watches have long fascinated collectors and vintage watch enthusiasts. Their eerie, self-luminous glow and historical significance make them prized possessions. But alongside their appeal, concerns about radiation exposure persist. Is it really dangerous to wear a radium-dialed watch? Let’s explore the history, risks, and collector’s value of these luminous timepieces.
🎥 Want to see more?
We've created a YouTube video on radium watches—exploring their history, how they work, Geiger counter readings, and safe handling tips.
🔗 Watch the video here
1. Radium and Dial Painting: The Beginning of Luminous Watches
The Discovery of Radium and Its Use in Watches
Radium was discovered in 1898 by Marie and Pierre Curie, and its unique ability to glow in the dark soon led to various applications—including watch dials. By the early 1900s, watchmakers realized that radium-based paint could make watch numerals and hands glow without requiring an external light source. This was a game-changer for military, aviation, and railroad workers who needed to read time in darkness.
Brands That Used Radium
Many well-known watch brands incorporated radium in their dials, including:
- Omega – Used radium dials extensively in military and civilian watches from the 1910s to the 1950s.
- Rolex – Early Rolex watches, including military-issued models, often featured radium lume.
- Longines – Produced pilot and military watches with radium-painted dials.
- Hamilton – Supplied the U.S. military with radium-lumed watches, particularly in World War II.
- Gruen, Elgin, and Waltham – Popular American brands that produced radium-dialed wristwatches and pocket watches.

Vintage Longines Military Pilot’s Watch, Swiss Made, Cal. 12.68N from 1940's
The Longines Calibre 12.68N wristwatch was introduced in 1939, at the outset of World War II, and quickly became one of the brand’s most enduring military timepieces. Produced in Switzerland and also assembled in the U.S. using Swiss-made components, this model was issued to U.S.
$2,000.00
See MoreThe Radium Girls and the Dark Side of Radium Dial Painting
In the 1910s and 1920s, radium dial painting was a booming industry. The workforce consisted largely of young women, later known as the Radium Girls. They were instructed to "lip-point" their brushes—moistening them with their lips—to create fine, precise lines on watch dials. Tragically, they were unaware of radium’s health hazards. Over time, many suffered severe radiation poisoning, leading to lawsuits that brought awareness to occupational safety and led to stricter regulations on radioactive materials.

2. Is It Really Dangerous to Wear a Radium-Dial Watch?
Radiation Exposure from Radium Watches
Radium emits ionizing radiation, primarily in the form of alpha particles, along with some beta and gamma radiation. However, alpha particles cannot penetrate glass, metal, or even human skin. The primary concern with radium-dial watches is ingestion or inhalation of radium dust, which can occur if the crystal is broken or the dial paint deteriorates.
Measuring the Risk
- External Exposure: Holding or wearing a radium-dialed watch poses minimal risk as long as the case and crystal are intact. The radiation levels at the watch surface are detectable with a Geiger counter but decrease significantly with distance.
- Internal Exposure: The real danger arises if radium particles are inhaled or ingested. This can happen when servicing an old radium watch, especially if the dial or hands are flaking. Watchmakers handling radium watches should take precautions, such as working in well-ventilated areas and wearing protective gear.
Safe Handling Tips
- Do not open the watch case unnecessarily.
- Avoid restoring or cleaning the dial unless done professionally.
- Store in a well-ventilated area, away from prolonged skin contact.
- If servicing is needed, ensure the watchmaker is experienced with radium dials.
3. Valuable Radium Watches Among Collectors
Despite safety concerns, radium-dialed watches remain highly sought after. Their historical significance, combined with the appeal of their original luminous properties, makes them valuable to collectors.
Notable Collectible Radium Watches
- Rolex Bubbleback (1930s-1950s) – Early Rolex models with radium dials are collector favorites, especially military-issued ones.
- Omega Military Watches (WWII Era) – Omega supplied various armed forces with radium-dialed timepieces.
- Longines Weems and Lindbergh Hour Angle Watches – Used by aviators, these models often had radium lume.
- WWII A-11 and Mark XI Military Watches – Issued by Hamilton, Elgin, and IWC, these radium-dialed watches were essential for pilots and soldiers.
- Gruen and Waltham Trench Watches (WWI Era) – Early wristwatches with radium dials, some featuring enamel numerals filled with radium paint.

Vintage Omega Chronometer,Rare Ref. 2410-1, Radium Dial, Cal. 30T2 RG from 1944
This vintage Omega Chronometer from 1944 is a highly sought-after example of Omega’s mid-century precision watchmaking, powered by the legendary Caliber 30T2 RG. As the chronometer-grade version of the iconic 30T2, this movement was specially adjusted for accuracy and represents one of Omega’s most respected hand-wound calibers of the era.
$6,800.00
See MoreDoes Radium Affect Value?
The presence of radium lume can increase the value of a watch if it remains intact and original. Collectors often prefer untouched dials, even if the radium has darkened over time. However, excessive wear, dial flaking, or cracked crystals can lower the value due to potential safety concerns.
4. Modern Perspectives: Should You Wear a Radium Watch?
While radium watches are part of horological history, whether to wear one is a personal choice. Some collectors wear them daily without concern, while others prefer to keep them as display pieces. If you do choose to wear one, take basic precautions:
- Do not wear it to sleep (reduces prolonged exposure).
- Keep the crystal intact (prevents radium dust exposure).
- Store it properly (away from other watches to avoid minor radiation exposure).
Alternatives to Radium Watches
If you love the look of vintage luminous watches but are concerned about safety, consider:
- Tritium Watches (1960s-1990s) – Less radioactive and still glows for years.
- Modern Luminova Watches – Safe, non-radioactive lume used today by brands like Rolex and Omega.
Conclusion
Radium-dial watches are a fascinating blend of history, craftsmanship, and scientific curiosity. While they do emit radiation, the risks are minimal if handled with care. For collectors, these timepieces are valuable relics of an era when glow-in-the-dark technology was revolutionary. Whether you wear one or simply admire them from a distance, understanding their history and safety helps appreciate these luminous watches responsibly.
FAQs
Q1. Are radium dial watches dangerous to wear?
A1. Wearing a radium-dial watch is generally safe as long as the crystal and case are intact. The main risk comes from inhaling or ingesting radium dust, not from external wear.
Q2. Do radium watches emit radiation?
A2. Yes. Radium emits alpha, beta, and small amounts of gamma radiation, but alpha particles cannot penetrate skin, metal, or glass.
Q3. Can radium from a watch harm you through the skin?
A3. No. Radium radiation does not penetrate intact skin. Risk arises only if radium particles enter the body through inhalation or ingestion.
Q4. Is it safe to sleep while wearing a radium watch?
A4. It’s generally advised not to sleep with a radium watch to avoid prolonged close exposure, even though the overall risk remains low.
Q5. Are radium dial watches still collectible?
A5. Yes. Radium-dial watches are highly collectible due to their historical significance, originality, and distinctive aging.
Q6. Does radium lume increase a watch’s value?
A6. Original radium lume can increase value if it’s intact and evenly aged. Flaking or damaged lume may reduce value due to safety concerns.
Q7. How can you tell if a watch has a radium dial?
A7. Common indicators include markings like “Radium,” “Ra,” or “Swiss Made” without “T,” strong Geiger counter readings, and lume that no longer glows brightly after charging.
Q8. What brands used radium lume in watches?
A8. Brands like Rolex, Omega, Longines, Hamilton, Gruen, Elgin, and Waltham widely used radium dials from the early 1900s to the 1950s.
Q9. Is it safe to service a radium watch at home?
A9. No. Opening or servicing radium watches at home is discouraged due to the risk of inhaling radium dust. Professional handling is strongly recommended.
Q10. How should radium watches be stored?
A10. Store them in a well-ventilated area, away from prolonged skin contact, and preferably separate from other watches.
Q11. Are tritium watches safer than radium watches?
A11. Yes. Tritium is significantly less radioactive and poses far lower health risks compared to radium.
Q12. Do radium watches still glow in the dark?
A12. The radium itself still emits radiation, but the phosphors have usually degraded, so most radium watches no longer glow strongly.
Q13. Should you avoid buying a radium-dial watch?
A13. Not necessarily. With proper handling and intact components, radium watches can be safely owned and enjoyed.
Q14. Why are collectors still interested in radium watches?
A14. Collectors value them for their originality, military history, early lume technology, and unique patina.
Q15. Are radium watches legal to own?
A15. Yes. Owning radium-dial watches is legal in most countries, though commercial reuse of radium lume is prohibited.